Displaying 1366 - 1380 of 7732
Resource
Basic page
The Covid-19 Messaging Working Group was formed to develop insights and implement strategies at scale for better communication on Covid-19. It includes economists, physicians, and epidemiologists.
Blog
Quality employment is one of the many ways people can graduate from poverty. Yet, unemployment remains is a problem that has only become more salient through the COVID-19 pandemic. Over the course of 2020, the Jobs and Opportunity Initiativehas funded more than twenty projects that seek to answer...
Evidence to Policy Case Study
Case study
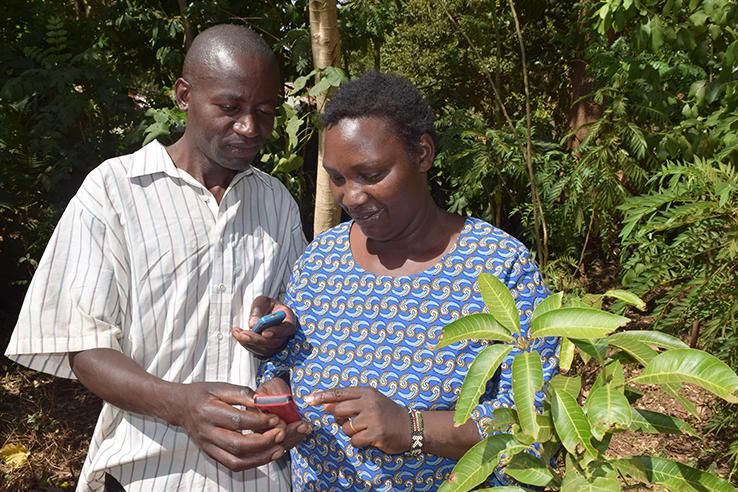
In this Evidence to Policy case study, see how Precision Development leveraged findings from two randomized evaluations to create and diffuse a new mobile-phone based model for agricultural extension.
Blog
J-PAL affiliate Kelsey Jack is leading a movement of climate-focused research within development economics and poverty alleviation through her own research and as co-chair of the King Climate Action Initiative.
Evaluation
In Mexico, researchers evaluated a math tutoring intervention and a cognitive behavioral therapy-based (CBT) program that aimed to encourage students to slow their decision-making processes and to improve academic readiness for secondary school students at risk of dropping out. The study found mixed effects on socio-emotional skills among students, and no effect on math test scores, though take-up was limited.
Blog
As the COVID-19 pandemic spread, 99 percent of the world’s 2.36 billion children faced some restrictions on movement, and 60 percent faced lockdown measures. With many schools and daycare facilities closed, who is taking care of the children?
Blog
J-PAL North America Executive Director Mary Ann Bates reflects on the last year in this post.
Evaluation
The proliferation of mobile money across low- and middle-income countries has led to increased availability of mobile payment systems, which can potentially allow more flexible payment terms for customers. Subsidies increased the use of mechanized desludgings, while pre-paid deposit requirements had no impact on their use. The flexibility of being able to save in advance in an earmarked savings account through the save-at-will treatment increased take-up through the program, but did so at the expense of take-up outside the program.
Evaluation
Researchers evaluated the impact of practicing sustained cognitive activity on cognitive endurance and school performance in Lucknow, India. Students that spent additional time engaging in sustained cognitive effort received higher grades in all of their classes, improved their performance on tests, and appeared more attentive in the classroom.
Evaluation
Low-income populations throughout the world often consume very few calories. At the time of this intervention in 2013, over 800 million people globally consumed fewer calories than were recommended to maintain a healthy weight. However, the impact of low caloric intake on economic productivity is not well researched. Researchers conducted a five-week randomized evaluation to test the impact of increased caloric intake on hours worked, earnings, and physical and cognitive ability for cycle-rickshaw drivers in Chennai, India. Drivers who consumed daily snacks worked and earned more and performed better on cognitive and physical tasks relative to drivers that received an equivalent value of cash. Supplemental survey data suggests that inaccurate beliefs and knowledge about the returns to calories and the caloric content of food may drive lower than recommended calorie consumption.
Page
Landing page
Blog
This note provides an overview of the evidence from randomized evaluations that has come out during the Covid-19 pandemic thus far to combat these barriers. These general lessons on increasing uptake of healthy behaviors and improving the delivery of health products and services may be of value in...
Person
Carmen Alvarez worked in Chile's Ministry of Social Development and the Innovation Division of the Ministry of Economy prior to joining J-PAL in 2013. She worked within J-PAL's Research Group for several months and is currently supporting the Policy Group.
Event
Join us daily from 11am-12:30pm EDT for this free, week-long webinar training series on Evaluating Social Programs. Throughout the week, these webinars will provide an introduction to why and how randomized evaluations can be used to rigorously measure social impact.