Crime, Violence, and Conflict
Crime and violence can hinder economic development and urban growth, and exacerbate governance challenges by fostering corruption and draining public sector resources. Poorly designed efforts to prevent or reduce crime and violence can also impose substantial social and economic costs on communities.
Key questions include the motivations behind criminal and violent behavior, ways of better understanding how social and political violence are organized, and evaluating the impact of policy responses designed to deter crime and violence or alleviate their negative effects. J-PAL affiliates’ research explores critical questions in this field, including how to cost-effectively improve police performance and perception, help at-risk youth reduce criminal and violent behavior, and reconcile communities in post-conflict fragile states.
In addition to supporting policymakers in applying evidence from randomized evaluations to their work, sector chairs and staff write policy insights that synthesize general lessons emerging from the research, condense results from evaluations in policy publications and evaluation summaries, and fund new research through the Crime and Violence Initiative.

File: Policy publication
Understanding Each Other: Improving Inter-Ethnic Cohesion in Schools in Turkey
An interactive classroom program encouraging students to consider one another’s perspectives in Turkey lowered peer violence, improved relationships between refugee and Turkish students, and increased prosocial behaviors like trust, cooperation, and altruism.

File: Policy publication
Improving Tolerance through Soccer in Post-ISIS Iraq
Promoting positive and cooperative contact helped Iraqi Christians displaced by ISIS build tolerance toward Muslim peers after conflict, but these effects did not generalize to the broader Muslim community.

In the news
Governance, Crime, and Conflict Initiative Evidence Wrap-up
What are the most promising strategies for reducing crime, violence, and conflict? The past decade has seen a dramatic expansion in the experimental literature designed to help answer this question. Moving beyond evaluations of individual programs, these studies seek to advance our understanding...

Evaluation
Contesting Criminal Gang Governance in Medellin: The Impacts of Intensive Municipal Governance and Community Organization on Gang Control and Governing of Neighborhoods
In partnership with the City of Medellín, researchers randomly introduced a program that intensified government outreach to gang-controlled neighborhoods. The study found no evidence that the city’s intervention reduced gang rule.

Blog
Preventing intimate partner violence by engaging men: Evidence from Unite for Better Life in Ethiopia
A growing body of evidence suggests that gender inequality, especially social norms that endorse violence against women, is one of the main drivers of IPV. What programs can effectively build more gender equitable attitudes and behaviors, and do these behaviors translate into reductions in violence...
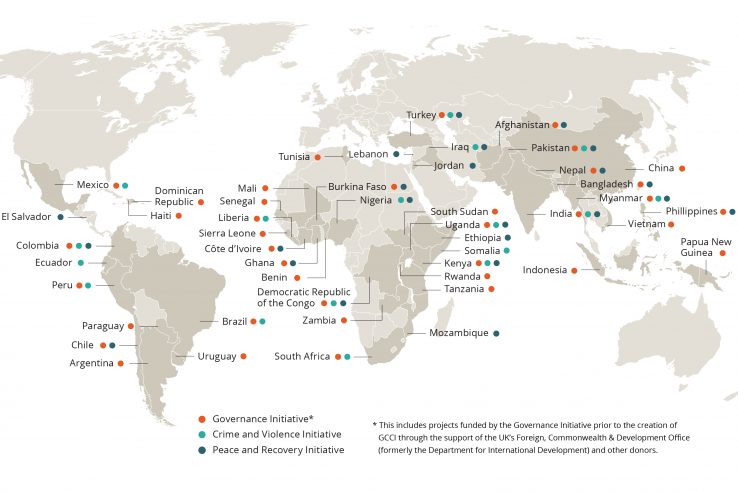
Blog
Pushing the boundaries of governance, crime, and conflict research: Innovations in research, measurement, and design
In 2017, J-PAL and IPA jointly launched the Governance, Crime, and Conflict Initiative to increase our understanding of effective policies to promote peace and good governance, reduce crime, and support individuals and communities recovering from conflict. With three years of research behind us, we...

Evaluation
Farmers and the fear of crime: Improving agricultural productivity through farm protection in Kenya
In Kenya, researchers matched farmers with subsidized, trained watchmen to evaluate the effect of improved farm security on farmers’ decision-making, agricultural productivity, and conflict with neighbors. Security was shown to increase and in response, farmers made different cropping, time use, and...

Policy insight
Preventing crime and violence with behavior change techniques
Crime and violence prevention programs that draw on behavior change techniques to address cognitive biases in decision-making have been effective in reducing criminal, violent, and antisocial behaviors. These generally low-cost interventions may help participants enhance their emotional regulation...





