A practical framework for evidence-informed policy: Addressing the generalizability puzzle
In recent decades, there has been a huge increase in the number of impact evaluations of different approaches to reducing poverty. Despite this, if you are a policymaker, it is unlikely that there will be a rigorous impact evaluation that answers precisely the question you are facing in precisely the location in which you are facing it. So how do you draw on the available evidence, both from your local context and from the global base of impact evaluations in other locations, to make the most informed decision?
In an article just published in the Stanford Social Innovation Review, J-PAL North America's Mary Ann Bates and I set out a practical generalizability framework that policymakers can use to decide whether a particular approach makes sense in their context. The key to the framework is that it breaks down the question “will this program work here?” into a series of questions based on the theory behind a program. Different types of evidence can then be used to assess the different steps in the generalizability framework.
Below is a generalizability framework for providing small incentives to nudge parents to immunize their children. The first steps require a local diagnosis of the problem, and need to be answered using local descriptive data as well as qualitative interviews and local institutional knowledge. The next steps are related to general lessons of human behavior, where studies from other contexts can be very valuable. The final steps are about local implementation, where local process monitoring evidence is key.
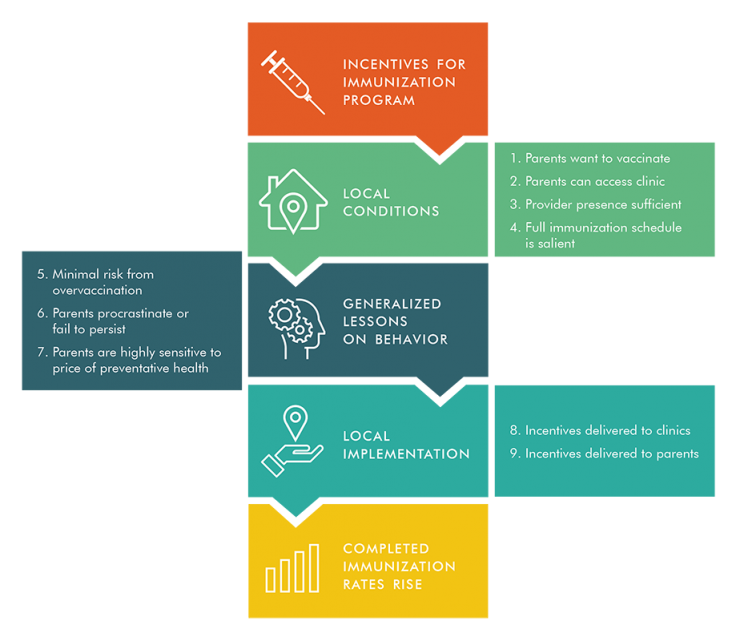
In the article we discuss our experience working alongside policymakers around the world to apply this framework to solve practical policy problems. We also show how this approach enables policymakers to draw on a much wider range of evidence than they might otherwise use: For example, with only two published RCTs on the immunization program above, there is a wealth of rigorous impact evaluation supporting the general behavioral lesson behind the program.
With this paper we seek to move the debate about generalizability of impact evaluations from its rather confused and unhelpful present to a more practical future. Read the full article at SSIR and add your comments.

